Category: pro
Python hosting: Host, run, and code Python in the cloud!
tutorials
Operaciones matemáticas
Puede utilizar el intérprete de Python como calculadora. Para ello simplemente iniciar Python sin un IDE y un nombre de archivo. Ejemplo:
Python 2.7.6 (por defecto, 22 de junio de 2015, 17:58:13) [GCC 4.8.2] de linux2 Tipo de "ayuda", "copyright", "créditos" o "licencia" para obtener más información. >>> 18 * 17 306 >>> 2 ** 4 16 >>>
Funciones matemáticas
Python soporta una amplia variedad de funciones matemáticas.
| Función | Devuelve | Ejemplo | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS(x) | Devuelve el valor absoluto de x. |
|
|
| CMP(x,y) |
Devuelve -1 Si x < y Devuelve 0 si x es igual a y Devuelve 1 Si x > y. |
|
|
| exp (x) | Devuelve la exponencial de x |
|
|
| Cienc | El logaritmo natural de x |
|
|
| log10(x) | El logaritmo en base 10 de x |
|
|
| Pow(x,y) | El resultado de x ** y |
|
|
| sqrt(x) | La raíz cuadrada de x |
|
IDEs de Python
Instalar un IDE de Python
Un Entorno de escritorio integrado (IDE) es un software para la programación. Además de edición de texto simple que tienen todo tipo de funciones tales como resaltado de sintaxis, completado de código, pestañas, un explorador de la clase y muchos más.
Python online intérpretes
Los intérpretes en línea no funcionen para todo pero funcionarán para la mayoría de los tutoriales para principiantes. Recomiendo usar un IDE desktop o el interprete oficial de Python.
Resumen de IDEs (sólo necesita uno)
| IDE | Autor | Plataforma | Descripción | Precio | Descargar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PyCharm | JetBrains | Windows, Mac OS X, Linux/UNIX | Python IDE. Características como: completación de código, inspecciones de código, error sobre la marcha destacando y soluciones rápidas | 89 € / 1er año. ($ 97,90) | Descarga PyCharm |
| Átomo (+ script plugin) | GitHub | Windows, Mac OS X, Linux/UNIX | Python IDE. Necesita descargar el plugin de secuencia de comandos después de instalar el átomo. | Gratis. | Descargar Atom. |
| Pythonista | OMZ:software | Apple iOS (iPhone, iPad) | Las características incluyen: resaltado de sintaxis, completado de código, sistema interactivo, módulos estándar y de iOS. | € 9. ($ 9,90) | Descargar Pythonista. |
| Eclipse con PyDev | Aleks Totic | Windows, Mac OS X, Linux/UNIX | Las características incluyen: sintaxis resaltado, refactorización de código, depuración gráfica y mucho más. | Gratis | Descargar |
| Eric Python IDE | Detlev Offenbach | Windows, Linux/UNIX | Las características incluyen: resaltado de sintaxis, autocompletado, clase navegador y más. | Gratis | Descargar |
| Wing IDE | Wingware | Windows, Mac OS X, Linux/UNIX | Características: Sintaxis resaltado, auto-completado, refactorización, pruebas unitarias y versión controlan. | $45 a $245 por usuario por licencia. | Descargar |
| Komodo IDE | Komodo | Windows, Mac OS X, Linux/UNIX | Características: Sintaxis, navegador de documentación, ejecutar código en línea, marcadores rápidos y mucho más. | € 40 a € 223. ($99 a $295). | Descargar |
| Skulpt | Skulpt | Web | Intérprete de Python | Gratis | Ejecutar en línea |
| Repl.it | Amjad Masad, Haya Odeh, Faris Masad y Max Shawabkeh. | Web | Intérprete de Python | Gratis | Ejecutar en línea |
| Ideone | Ideone | Web | Intérprete de Python | Gratis | Ejecutar en línea |
| CodePad | Hazel de Steven | Web | Intérprete de Python | Gratis | Ejecutar en línea |
SL4A: Android Python Scripting
Python scripts can be run on Android using the Scripting Layer For Android (SL4A) in combination with a Python interpreter for Android.
Related courses:
You may like:
SL4A
The SL4A project makes scripting on Android possible, it supports many programming languages including Python, Perl, Lua, BeanShell, JavaScript, JRuby and shell. The SL4A project has a lot of contributors from Google but it is not an official Google project.
Scripts can access Android specific features such as calling, text message (SMS), take picture, text to speech, bluetooth and many more.
In this article you will learn how to run Python on Android devices using SL4A.
SL4A is designed for developers
Keep in mind that SL4A is designed for developers and in alpha quality software.
Install SL4A

First enable installation of programs from unknown sources. By default Android devices can only install apps from the Google Play Store.
You have to enable the permission ‘Install from Unknown Sources’, by going to Settings -> Security -> Unknown Sources and tap the box.
After you have have updated these settings donwload the SL4A APK. Visit https://github.com/kuri65536/sl4a on your Android device and download the SL4A APK (or use the QR code on the right).
Once downloaded an installation menu will popup, requesting all permissions on your Android device.
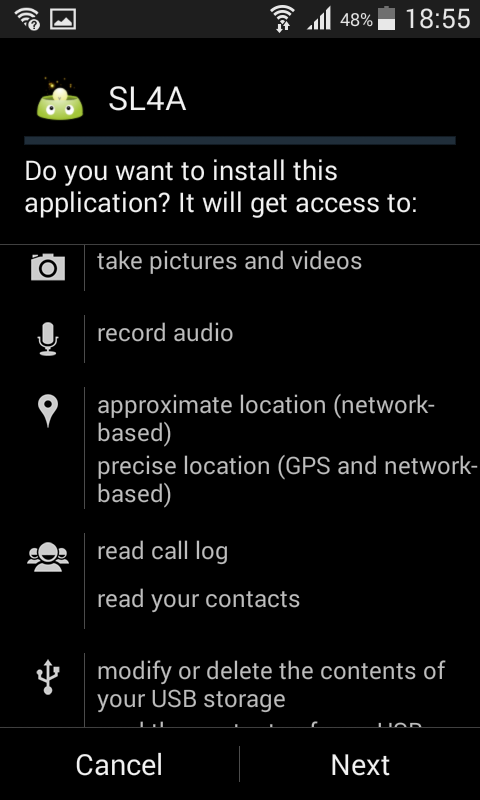
Install Python 3 for Android

Install the Py4A app. The Python for Android app is built to run solely on
Android devices. You should use this app together with SL4A.
You can pick any version of Py4A, but bare in mind the supported version on Android:
- Python 2 requires Android Device >= 1.6
- Python 3 requires Android Device >= 2.3.1
The git repository is: https://github.com/kuri65536/python-for-android/releases
You could also use the QR code on the right using a QR scanner on your Android device.
Once Py4A is installed, start the app and press install. This will install the Python interpreter.
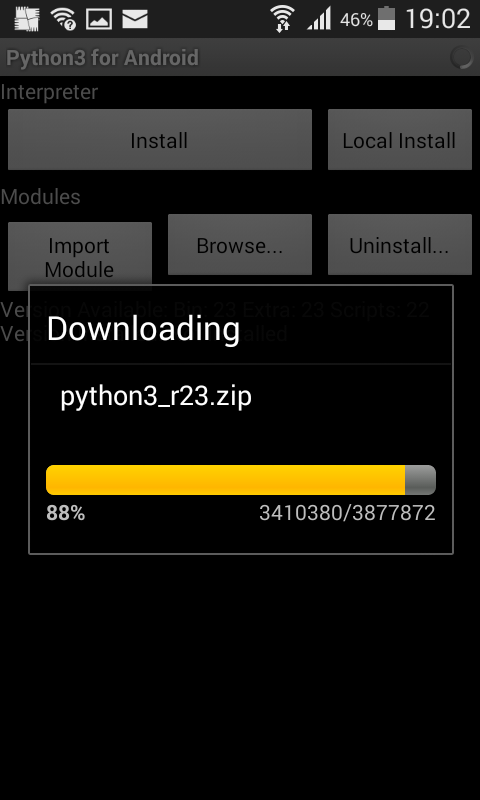
SL4A
Open SL4A again. Many scripts will appear (in a list). You can now run Python scripts on your Android Device!
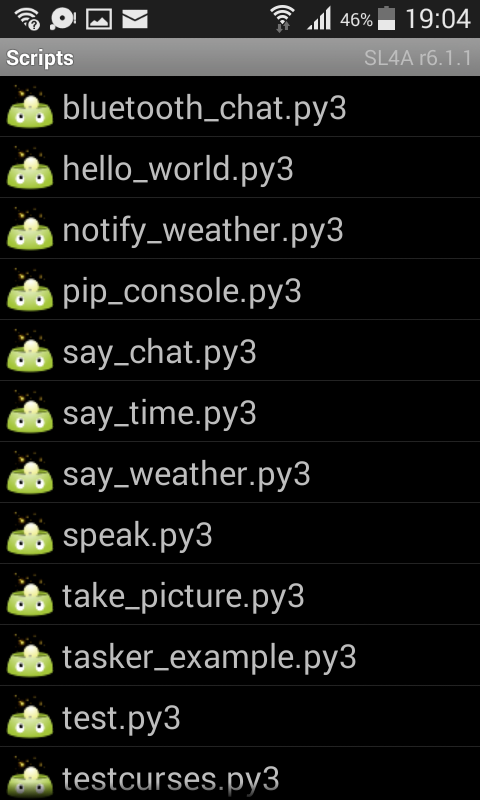
Press on a program such as speak.py A little popup will be shown. Pressing on the terminal icon will start the Python script.
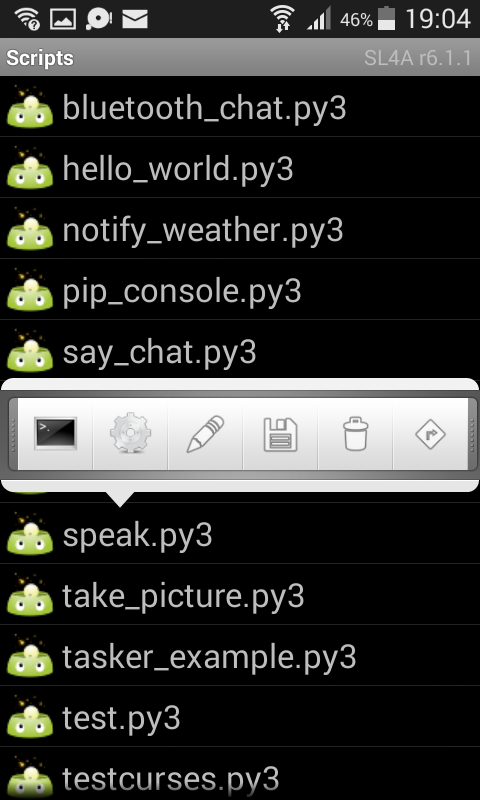
The third button (the pencil) will open an editor. This is not a full blown IDE but a simple editor.
It doesn’t have syntax highlighting.
Scripting on Android
You may prefer your favorite Python editor whatever it may be (vim/emacs fans here? PyCharm? Atom?)
All scripts are stored in /sl4a/scripts/
Note: File extension
If you installed the Python 3 interpreter, the programs will show with a .py3 extension instead of a .py extension.
A simple program (Spaceship Launch):
"""TTS Rocket Launch.""" __author__ = 'Frank <[email protected]>' import android droid = android.Android() message = "Python on Android" droid.ttsSpeak(message) for i in range(10,0,-1): droid.ttsSpeak(str(i)) droid.ttsSpeak("We have lift off!") droid.ttsSpeak("rrrrrr") |
More examples:
http://www.mattcutts.com/blog/android-barcode-scanner/
https://github.com/damonkohler/sl4a/blob/wiki/Tutorials.md
HTTP – Parse HTML and XHTML
In this article you will learn how to parse the HTML (HyperText Mark-up Language) of a website. There are several Python libraries to achieve that. We will give a demonstration of a few popular ones.
Beautiful Soup – a python package for parsing HTML and XML
This library is very popular and can even work with malformed markup. To get the contents of a single div, you can use the code below:
from BeautifulSoup import BeautifulSoup import urllib2 # get the contents response = urllib2.urlopen('http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Python_(programming_language)') html = response.read() parsed_html = BeautifulSoup(html) print parsed_html.body.find('div', attrs={'class':'toc'}) |
This will output the HTML code of within the div called ‘toc’ (table of contents) of the wikipedia article. If you want only the raw text use:
print parsed_html.body.find('div', attrs={'class':'toc'}).text |
If you want to get the page title, you need to get it from the head section:
print parsed_html.head.find('title').text |
To grab all images URLs from a website, you can use this code:
from BeautifulSoup import BeautifulSoup import urllib2 url = 'http://www.arstechnica.com/' data = urllib2.urlopen(url).read() soup = BeautifulSoup(data) links = soup.findAll('img', src=True) for link in links: print(link["src"]) |
To grab all URLs from the webpage, use this:
from BeautifulSoup import BeautifulSoup import urllib2 url = 'http://www.arstechnica.com/' data = urllib2.urlopen(url).read() soup = BeautifulSoup(data) links = soup.findAll('a') for link in links: print(link["href"]) |
PyQuery – a jquery like library for Python
To extract data from the tags we can use PyQuery. It can grab the actual text contents and the html contents, depending on what you need. To grab a tag you use the call pq(‘tag’).
from pyquery import PyQuery import urllib2 response = urllib2.urlopen('http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Python_(programming_language)') html = response.read() pq = PyQuery(html) tag = pq('div#toc') # print the text of the div print tag.text() # print the html of the div print tag.html() |
To get the title simply use:
tag = pq('title') |
HTMLParser – Simple HTML and XHTML parser
The usage of this library is very different. With this library you have to put all your logic in the WebParser class. A basic example of usage below:
from HTMLParser import HTMLParser import urllib2 # create parse class WebParser(HTMLParser): def handle_starttag(self, tag, attrs): print "Tag: " + tag # get the contents response = urllib2.urlopen('http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Python_(programming_language)') html = response.read() # instantiate the parser and fed it some HTML parser = WebParser() parser.feed(html) |
Python Web Development
Introduction
Web apps are often created using a framework. Frameworks make it easier to develop web apps that are scalable, reliable and maintainable. It avoids recreating the same code over and over again.
Common features are:
- URL Routing
- Output templates
- Database management
- Session management
- Security against common attacks
A framework may offer some or all of these features.
For example, the Flask web application framework does not have database support and you would need a separate module to use a database. The Django web application framework supports databases by default.
Why use a web framework?
As you are doing web development, you want to avoid spending time on programming things that have already been solved. On the other hand, if you are an experienced web developer a web framework may not offer everything you need.
What Python web frameworks exist?
Django and Flask are the most popular web frameworks. However, you may want to evaluate the frameworks. An overview:
The most popular python web application framework is Django, followed by Flask.
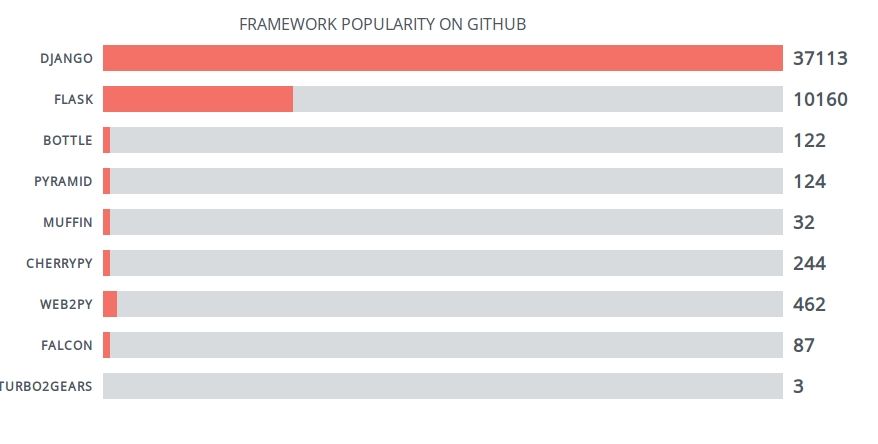
Django
Django is the most used Python web framework. It takes care of many things so you can focus on the web app development. Sites built withDjango have dealt with high traffic spikes such as 50 thousands hits per second.
Database access is achieved through an Object-relational mapper: You define your data models in Python and Django deals with the actual database management systems (SQL). However, if you need to you can write your own SQL Queries with Django. URL routing is supported by Django. It encourages beautiful URL design such as ending without .php or .asp.
Features:
- Object-relational mapper
- URLs routing and views
- Template engine
- Forms
- Authentication
- Admin
- Internationalization
- Security
If you want to know more about Django, read here.
Flask

Flask is a Python micro framework which is modular by design. The framework is intended to build web apps. Flask does not have a specific database system or ORM system. If you want to use a database, you’ll have to use extensions. Flask is often combined with SQLAlchemy for database use.
Flask is very easy to get running, a minimal app would be:
from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/') def hello_world(): return 'Hello World!' if __name__ == '__main__': app.run() |
The framework supports URL routing, template (using Jinja2), session management and has some out of the box security.
Features:
- URL Routing and views
- Template engine
- Session management
- Logging
If you want to know more about Flask, read here.
Python Hosting
To run your app on the web, you will need hosting. Unless you want to do hosting yourself, you need a party to host.
Hosting servers:
Django Getting started
Django is a high-level Python Web framework that takes care of much of the hassle of Web development, so you can focus on writing your app without needing to reinvent the wheel.
In this tutorial you will learn how to setup a basic Django web app.
Related course
Intro to Django Python Web Apps
Django tutorial
Install Django using:
pip install Django==1.7.1 |
Once installed, create the directory /django-hello/ for your app. In this directory create the file hello.py with this contents:
#!/usr/bin/env python import sys from django.conf import settings from django.conf.urls import patterns from django.http import HttpResponse from django.core.management import execute_from_command_line settings.configure( DEBUG=True, SECRET_KEY='asecretkey', ROOT_URLCONF=sys.modules[__name__], ) def index(request): return HttpResponse('Hello, World') urlpatterns = patterns('', (r'^hello/$', index), ) if __name__ == "__main__": execute_from_command_line(sys.argv) |
Execute the script using:
python hello.py runserver |
A HTTP Django server will start and if you open http://127.0.0.1:8000/hello/
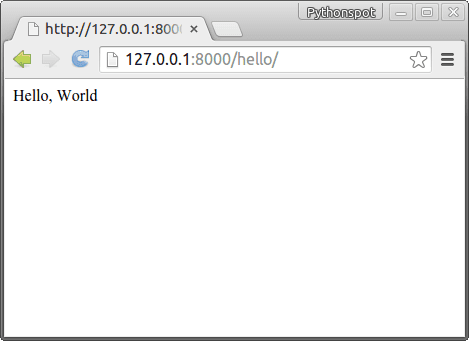
Django code explanation:
The top lines import the Django library:
from django.conf import settings from django.conf.urls import patterns from django.http import HttpResponse from django.core.management import execute_from_command_line |
If you open the link /hello/, the webserver will call the index() function. We map the url to the function using:
urlpatterns = patterns('', (r'^hello/$', index), ) |
In Django we have url friendly urls. This means you do not have a url that ends in /id=1359835, but instead we have the directory as name. Finally, we set some default settings using settings.configure.


