Strings
Python hosting: Host, run, and code Python in the cloud!
Variablen in Mathematik besitzen oft bestimmte Werten wie Zahlen.
Doch müsst das nicht immer so sein, manchmal können variablen ein Zeichen oder Zeichenkette (Strings) besitzen.
Python Programming Bootcamp: Go from zero to hero
Strings
Ein String kannst du als nummerierte Zeichenkette sehen:
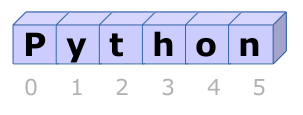
Jeder Zeichen in einem String kannst du mit ein Index nummern erreichen.
Eine Sammlung in Python startet immer mit der 0-index.
|
Es gibt drei weisen für String Definition: single (‘), double quotes (“) oder triple quotes (“””).
Zum Beispiel:
|
Du kannst das Resultat von einer Methode speichern, wie s = s.replace(“world”,”python”).
String slices
Die Syntax für ein teil -string ist:
|
Der startIndex ist null (erste Zeichen) oder mehr. Als du der startIndex nicht spezifiziert ist es immer null. Der variablen pastIndex ist die Länge einer String plus eins.
|
Strings bearbeiten
Es gibt verschiedene weisen für String Bearbeitung.
|
Comparison, contains and concatenation
Der Operator (==) kannst du benutzen für Vergleich von zwei Strings. Das in keyword kannst du benutzen für suchen in einem String. Du kannst ein String an ein String hinzufügen mit der (+) Operator.
|
Escape- oder Fluchtzeichen
Es gibt speciale Zeichen in Python, wie der ‘\n’ fuer neuregeln.
|
| 'Escape' Zeichen | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
| \n | Neuregeln. |
| \" | Quotes. |
| \' | Single Quote. |
| \t | Tab. |
| \\ | Backslash. |
| Method with description |
|---|
|
capitalize(str) Returns first letter capitalized string. |
|
count(str) Count the frequency of the word str. It can also be applied to words: s.count("Hello") |
|
find(str) Find the position of the first occurence. |
|
index(str) Find the position of the first occurence, raise exception if not found. |
|
isdecimal() Returns true if string is decimal. |
|
isdigit() Returns true if string contains digits only. |
|
isnumeric() Returns true if string contains numeric only. |
|
lower() Returns string in lowercase. |
|
len(str) Returns the length of str. |
|
upper() Returns string in uppercase. |
|
replace(old, new) Replaces the first argument with the second argument. |

Leave a Reply: