Category: Network
python urllib
Websites can be accessed using the urllib module. You can use the urllib module to interact with any website in the world, no matter if you want to get data, post data or parse data.
If you want to do web scraping or data mining, you can use urllib but it’s not the only option. Urllib will just fetch the data, but if you want to emulate a complete web browser, there’s also a module for that.
Related course:
Web Scraping in Python with BeautifulSoup & Scrapy Framework
python urllib
Download website
We can download a webpages HTML using 3 lines of code:
|
The variable html will contain the webpage data in html formatting. Traditionally a web-browser like Google Chrome visualizes this data.
Web browser
A web-browsers sends their name and version along with a request, this is known as the user-agent. Python can mimic this using the code below. The User-Agent string contains the name of the web browser and version number:
import urllib.request |
Parsing data
Given a web-page data, we want to extract interesting information. You could use the BeautifulSoup module to parse the returned HTML data.
You can use the BeautifulSoup module to:
There are several modules that try to achieve the same as BeautifulSoup: PyQuery and HTMLParser, you can read more about them here.
Posting data
The code below posts data to a server:
|
how to get all page urls from a website
Web scraping is the technique to extract data from a website.
The module BeautifulSoup is designed for web scraping. The BeautifulSoup module can handle HTML and XML. It provides simple method for searching, navigating and modifying the parse tree.
Related course:
Browser Automation with Python Selenium
Get links from website
The example below prints all links on a webpage:
|
It downloads the raw html code with the line:
|
A BeautifulSoup object is created and we use this object to find all links:
|
Extract links from website into array
To store the links in an array you can use:
|
Function to extract links from webpage
If you repeatingly extract links you can use the function below:
|
Related course:
Browser Automation with Python Selenium
python parse html
In this article you will learn how to parse the HTML (HyperText Mark-up Language) of a website. There are several Python libraries to achieve that. We will give a demonstration of a few popular ones.
Related courseBeautiful Soup - a python package for parsing HTML and XML
This library is very popular and can even work with malformed markup. To get the contents of a single div, you can use the code below:
from BeautifulSoup import BeautifulSoup |
This will output the HTML code of within the div called ‘toc’ (table of contents) of the wikipedia article. If you want only the raw text use:
print parsed_html.body.find('div', attrs={'class':'toc'}).text |
If you want to get the page title, you need to get it from the head section:
print parsed_html.head.find('title').text |
To grab all images URLs from a website, you can use this code:
from BeautifulSoup import BeautifulSoup |
To grab all URLs from the webpage, use this:
from BeautifulSoup import BeautifulSoup |
PyQuery - a jquery like library for Python
To extract data from the tags we can use PyQuery. It can grab the actual text contents and the html contents, depending on what you need. To grab a tag you use the call pq(‘tag’).
from pyquery import PyQuery |
To get the title simply use:
tag = pq('title') |
HTMLParser - Simple HTML and XHTML parser
The usage of this library is very different. With this library you have to put all your logic in the WebParser class. A basic example of usage below:
from HTMLParser import HTMLParser |
python download file from url
The urllib2 module can be used to download data from the web (network resource access). This data can be a file, a website or whatever you want Python to download. The module supports HTTP, HTTPS, FTP and several other protocols.
In this article you will learn how to download data from the web using Python.
Related courseDownload text
To download a plain text file use this code:
import urllib2 |
We get a response object using the urllib2.urlopen() method, where the parameter is the link. All of the file contents is received using the response.read() method call. After calling this, we have the file data in a Python variable of type string.
Download HTML
This will request the html code from a website. It will output everything to the screen.
import urllib2 |
Download file using Python
You can save the data to disk very easily after downloading the file:
import urllib2 |
The first part of the code downloads the file contents into the variable data:
|
The second part stores it into a file (this file does not need to have the same filename)
|
The ‘w’ parameter creates the file (or overwrites if it exists). You can read more about writing files here.
Related coursepython socket
python ftp client
This article will show you how to use the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) with Python from a client side perspective. We use ftplib, a library that implements the FTP protocol. Using FTP we can create and access remote files through function calls.
Related course
Python Programming Bootcamp: Go from zero to hero
Directory listing
FTP is a protocol for transferring files between systems over a TCP network. It was first developed in 1971 and has since been widely adopted as an effective way to share large files over the internet. File Transfer Protocol (often abbreviated FTP) is an application- layer protocol.
We can list the root directory using this little snippet:
import ftplib |
This will output the directory contents. in a simple console style output. If you want to show a specific directory you must change the directory after connecting with the ftp.cwd(‘/‘) function where the parameter is the directory you want to change to.
import ftplib |
Download file
To download a file we use the retrbinary() function. An example below:
import ftplib |
Uploading files
We can upload files using the storlines() command. This will upload the file README.nluug in the main directory. If you want to upload in another directory combine it with the cwd() function.
import ftplib |
Related course
Python Programming Bootcamp: Go from zero to hero
Other functions
For other functions please refer to the official library documentation.
pop3
In this tutorial you will learn how to receive email using the poplib module. The mail server needs to support pop3, but most mail servers do this. The Post Office Protocol (POP3) is for receiving mail only, for sending you will need the SMTP protocol.
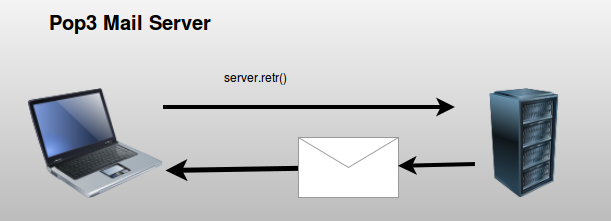
Related course:
Python Programming Bootcamp: Go from zero to hero
Meta Data
Every email will contain many variables, but these are the most important ones:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| message-id | unique identifier |
| from | where did the email come from? |
| to | where was the email sent to? |
| date | date |
| subject | Email subject. |
|
The program below gets 10 emails from the server including mail header
|
Related course:
Python Programming Bootcamp: Go from zero to hero
