python graph
Python hosting: Host, run, and code Python in the cloud!
Introduction
A graph in mathematics and computer science consists of “nodes” which may or may not be connected with one another. Connections between nodes are called edges. A graph can be directed (arrows) or undirected. The edges could represent distance or weight.
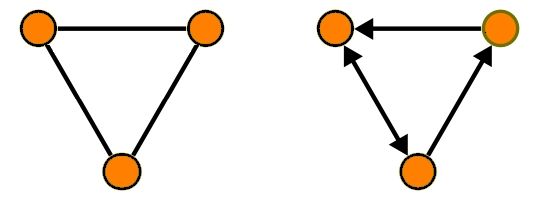
default graph (left), directed graph (right)
Python does not have a graph data type. To use graphs we can either use a module or implement it ourselves:
- implement graphs ourselves
- networkx module
Related course
Python Programming Bootcamp: Go from zero to hero
Graph in Python
A directed graph can be defined as:
#!/usr/bin/env python |
Graphs using networkx
The networkx software module has support for creating, manipulating graphs.
#!/usr/bin/env python |
Result:
Nodes: [‘A’, ‘C’, ‘B’]
Edges: [(‘A’, ‘C’), (‘A’, ‘B’), (‘C’, ‘B’)]
Posted in Beginner

Leave a Reply:
import networkx as nx
dosen't work syntaxerror
Install the networkx module using: pip install networkx
You will need to install virtualenv on OSX otherwise you will have trouble installing networkx module.