tkinter askquestion
Python hosting: Host, run, and code Python in the cloud!
Tkinter supports showing a message box. Tkinter is a GUI library for Python, it lets you make desktop applications.
The implementation you need depends on your Python version, you should use Python 3 or newer (2 is legacy).
To test your Python version:
python -- version |
Related course
Tkinter question dialog
Tkinter can be used to crete a prompt that ask the users a question.
Python 2.x
The Python 2.x version:
import Tkinter |
Python 3
The Python 3.x version:
|
Result:
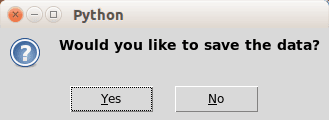
Tkinter message boxes
This code will open some Tkinter question boxes:
Python 2.7
The Python 2.x version:
import Tkinter |
Python 3
The Python 3.x version:
|
Result:
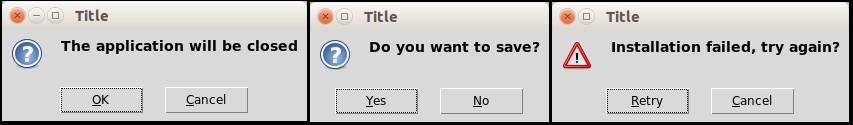
Posted in Tk

Leave a Reply: