Category: gui
Python hosting: Host, run, and code Python in the cloud!
wxPython menu
Most desktop applications have a window menu. They may look different depending the operating system.
wxPython will make every desktop application look like a native app. If you want the same appearance on every platform consider using another GUI framework.
wxPython menu
The code below will create a menubar in your wxPython window:
#!/usr/bin/python import wx app = wx.App() frame = wx.Frame(None, -1, 'win.py') frame.SetDimensions(0,0,200,50) # Setting up the menu. filemenu= wx.Menu() filemenu.Append(101, "Open", "Open") filemenu.Append(102, "Save", "Save") filemenu.Append(wx.ID_ABOUT, "About","About") filemenu.Append(wx.ID_EXIT,"Exit","Close") # Creating the menubar. menuBar = wx.MenuBar() menuBar.Append(filemenu,"File") # Adding the "filemenu" to the MenuBar frame.SetMenuBar(menuBar) # Adding the MenuBar to the Frame content. frame.Show() app.MainLoop() |
A menu in wxPython is simple a wx.MenuBar().
This menu alone will not do anything, it needs to have several sub-menus such as a File menu. A sub-menu can be created with wx.Menu() which in turn has several items.
Finally, we set the frame’s menubar to the menubar we created.
wxPython has some default ids such as wx.ID_ABOUT and wx.ID_EXIT, which are both just integers. You can define your own ids as we did (101, 102).
wxPython tabs
While we did not heavily use object orientation for the wxPython series yet for simplicity reasons, we cannot go around it. In this tutorial you will learn how to create a tab interface with wxPython.
The class Mainframe creates the frame as we did in the previous examples. The other classes are the contents of the tabs. We create a panel and notebook (tab holder) in the main frame. Then we create tab objects :
tab1 = TabOne(nb) tab2 = TabTwo(nb) ... |
which we attach to the tab holder using:
nb.AddPage(tab1, "Tab 1") nb.AddPage(tab2, "Tab 2") ... |
Full code:
import wx # Define the tab content as classes: class TabOne(wx.Panel): def __init__(self, parent): wx.Panel.__init__(self, parent) t = wx.StaticText(self, -1, "This is the first tab", (20,20)) class TabTwo(wx.Panel): def __init__(self, parent): wx.Panel.__init__(self, parent) t = wx.StaticText(self, -1, "This is the second tab", (20,20)) class TabThree(wx.Panel): def __init__(self, parent): wx.Panel.__init__(self, parent) t = wx.StaticText(self, -1, "This is the third tab", (20,20)) class TabFour(wx.Panel): def __init__(self, parent): wx.Panel.__init__(self, parent) t = wx.StaticText(self, -1, "This is the last tab", (20,20)) class MainFrame(wx.Frame): def __init__(self): wx.Frame.__init__(self, None, title="wxPython tabs example @pythonspot.com") # Create a panel and notebook (tabs holder) p = wx.Panel(self) nb = wx.Notebook(p) # Create the tab windows tab1 = TabOne(nb) tab2 = TabTwo(nb) tab3 = TabThree(nb) tab4 = TabFour(nb) # Add the windows to tabs and name them. nb.AddPage(tab1, "Tab 1") nb.AddPage(tab2, "Tab 2") nb.AddPage(tab3, "Tab 3") nb.AddPage(tab4, "Tab 4") # Set noteboook in a sizer to create the layout sizer = wx.BoxSizer() sizer.Add(nb, 1, wx.EXPAND) p.SetSizer(sizer) if __name__ == "__main__": app = wx.App() MainFrame().Show() app.MainLoop() |
Output:

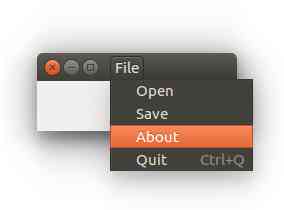
Tk menubar
The Tkinter toolkit comes with all the basic widgets to create graphical applications. Almost every app has a main menu. As expected, Tkinter supports adding a main menu to your application window.
The screenshot below demonstrates a Tkinter based menu:
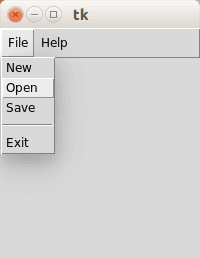
Related course
Tkinter menubar
You can create a simle menu with Tkinter using the code below. Every option (new, open, save.. ) should have its own callback.
from Tkinter import * def donothing(): x = 0 root = Tk() menubar = Menu(root) filemenu = Menu(menubar, tearoff=0) filemenu.add_command(label="New", command=donothing) filemenu.add_command(label="Open", command=donothing) filemenu.add_command(label="Save", command=donothing) filemenu.add_separator() filemenu.add_command(label="Exit", command=root.quit) menubar.add_cascade(label="File", menu=filemenu) helpmenu = Menu(menubar, tearoff=0) helpmenu.add_command(label="Help Index", command=donothing) helpmenu.add_command(label="About...", command=donothing) menubar.add_cascade(label="Help", menu=helpmenu) root.config(menu=menubar) root.mainloop() |
We create the menubar with the call:
menubar = Menu(root) |
where root is a Tk() object.
A menubar may contain zero or more submenus such as the file menu, edit menu, view menu, tools menu etcetera.
A submenu can be created using the same Menu() call, where the first argument is the menubar to attach to.
filemenu = Menu(menubar, tearoff=0) menu = Menu(menubar, tearoff=0) |
Individual options can be added to these submenus using the add_command() method:
filemenu.add_command(label="New", command=donothing) filemenu.add_command(label="Open", command=donothing) filemenu.add_command(label="Save", command=donothing) |
In the example we created the callback function donothing() and linked every command to it for simplicity. An option is added using the add_comment() function. We call add_cascade() to add this menu list to the specific list.
Tk widgets
Tkinter has several widgets including:
- Label
- EditText
- Images
- Buttons (Discussed before)
In this article we will show how to use some of these Tkinter widgets. Keep in mind there’s a slight difference between Tkinter for Python 2.x and 3.x
Related course
Label
To create a label we simply call the Label() class and pack it. The numbers padx and pady are the horizontal and vertical padding.
from Tkinter import * root = Tk() root.title('Python Tk Examples @ pythonspot.com') Label(root, text='Python').pack(pady=20,padx=50) root.mainloop() |
EditText (Entry widget)
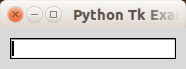
To get user input you can use an Entry widget.
from Tkinter import * root = Tk() root.title('Python Tk Examples @ pythonspot.com') var = StringVar() textbox = Entry(root, textvariable=var) textbox.focus_set() textbox.pack(pady=10, padx=10) root.mainloop() |
Result:
Images
Tk has a widget to display an image, the PhotoImage. It is quite easy to load an image:
from Tkinter import * import os root = Tk() img = PhotoImage(file="logo2.png") panel = Label(root, image = img) panel.pack(side = "bottom", fill = "both", expand = "yes") root.mainloop() |
Result:

GUI editor
An overview of Tkinter GUI editors can be found here: http://wiki.tcl.tk/4056
Tkinter tkFileDialog module
tkFileDialog is a module with open and save dialog functions.
Instead of implementing those in Tkinter GUI on your own.
Related courses
Overview
An overview of file dialogs:
| Function | Parameters | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| .askopenfilename | Directory, Title, Extension | To open file: Dialog that requests selection of an existing file. |
| .asksaveasfilename | Directory, Title, Extension) | To save file: Dialog that requests creation or replacement of a file. |
| .askdirectory | None | To open directory |
Tkinter Open File
The askopenfilename function to creates an file dialog object. The extensions are shown in the bottom of the form (Files of type). The code below will simply show the dialog and return the filename. If a user presses cancel the filename is empty. On a Windows machine change the initialdir to “C:\”.
Python 2.7 version:
from Tkinter import *from Tkinter import * import Tkinter, Tkconstants, tkFileDialog root = Tk() root.filename = tkFileDialog.askopenfilename(initialdir = "/",title = "Select file",filetypes = (("jpeg files","*.jpg"),("all files","*.*"))) print (root.filename) |
Python 3 version:
from tkinter import filedialog from tkinter import * root = Tk() root.filename = filedialog.askopenfilename(initialdir = "/",title = "Select file",filetypes = (("jpeg files","*.jpg"),("all files","*.*"))) print (root.filename) |
Here is an example (on Linux):
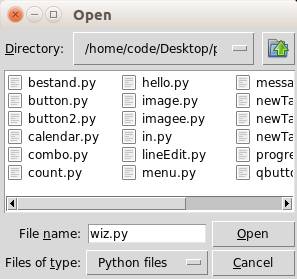
Tkinter Save File
The asksaveasfilename function prompts the user with a save file dialog.
Python 2.7 version
from Tkinter import * import Tkinter, Tkconstants, tkFileDialog root = Tk() root.filename = tkFileDialog.asksaveasfilename(initialdir = "/",title = "Select file",filetypes = (("jpeg files","*.jpg"),("all files","*.*"))) print (root.filename) |
Python 3 version
from tkinter import filedialog from tkinter import * root = Tk() root.filename = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(initialdir = "/",title = "Select file",filetypes = (("jpeg files","*.jpg"),("all files","*.*"))) print (root.filename) |
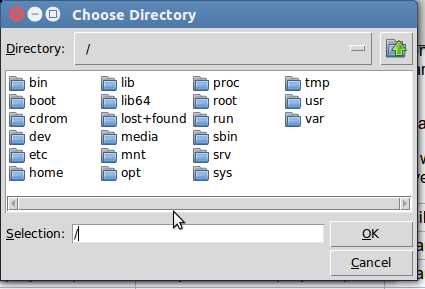
Tkinter Open Directory
The askdirectory presents the user with a popup for directory selection.
Python 2.7 version
from Tkinter import * import Tkinter, Tkconstants, tkFileDialog root = Tk() root.directory = tkFileDialog.askdirectory() print (root.directory) |