pandas filter
Python hosting: Host, run, and code Python in the cloud!
Filtering rows in a DataFrame with Python’s pandas library is a fundamental task for anyone involved in Data Analysis. It allows us to narrow down our dataset to the specific rows that are relevant for our analysis.
If you’re looking to enhance your data analysis skills, consider this Data Analysis with Python Pandas course.
Filter Using the Query Method
Within pandas, a DataFrame’s columns can be filtered using boolean expressions. The query() function is an integral part of the DataFrame that facilitates this.
For example, let’s demonstrate by importing necessary libraries and creating a simple DataFrame:
1 | import pandas as pd |
The above code generates a DataFrame that appears like: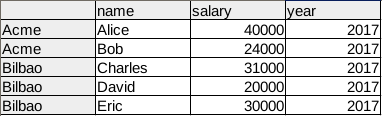
With our DataFrame set, we can utilize the query() function. For instance, if we want to filter out employees with a salary greater than 30,000:
1 | df_filtered = df.query('salary>30000') |
The result would display employees that fit the above criteria: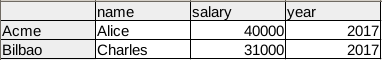
If you’d like to see the code for both creating the DataFrame and applying the filter in one place:
1 | import pandas as pd |
Filter Using Indexing and Method Chaining
Another approach to filtering data in pandas is through indexing with boolean expressions. This can sometimes provide more flexibility than the query() method:
1 | df_filtered = df[(df.salary >= 30000) & (df.year == 2017)] |
This will return rows where the salary is 30,000 or higher and the year is 2017: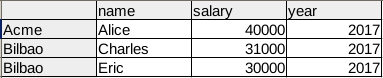
In conclusion, pandas offers multiple ways to filter DataFrames to better analyze and present your data. Whether you’re using the query() function or indexing, mastering these techniques will significantly improve your data analysis capabilities.
For a deep dive into pandas and data analysis, check out this Data Analysis with Python Pandas course.

Leave a Reply: