python tree
Python hosting: Host, run, and code Python in the cloud!
Introduction
In computer science, a tree is a data structure that is modeled after nature. Unlike trees in nature, the tree data structure is upside down: the root of the tree is on top. A tree consists of nodes and its connections are called edges. The bottom nodes are also named leaf nodes. A tree may not have a cycle.
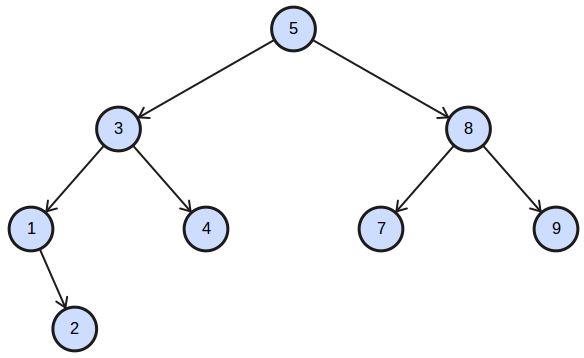
Python does not have built-in support for trees.
Related Course:Binary tree
A binary tree is a data structure where every node has at most two children (left and right child). The root of a tree is on top. Every node below has a node above known as the parent node.We define a class thee which has a left and right attribute. From this binary tree we define the root (top of the three) and a left and right node.
#!/usr/bin/env python |
You could then further create the tree like this:
#!/usr/bin/env python |
Posted in Beginner

Leave a Reply:
Hello
Is there a way to dinamically assign the number of children branches for each parent branch?
Thanks!
Hi Miguel!
Yes, it is possible to assign the number of children using a method, but if a tree has more than two children we can no longer call it binary.
I created some code: