Python hosting : Host, run, and code Python in the cloud!
Matplotlib can create 3d plots. Making a 3D scatterplot is very similar to creating a 2d, only some minor differences. On some occasions, a 3d scatter plot may be a better data visualization than a 2d plot. To create 3d plots, we need to import axes3d.
Related course:
Introduction
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
Give the data a z-axis and set the figure to 3d projection:
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d' )
Matplotlib
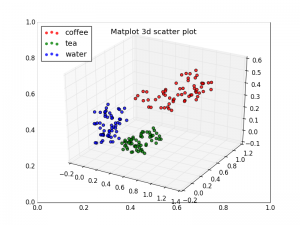
3d scatterplot Complete 3d scatterplot example below:
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3dN = 60 g1 = (0.6 + 0.6 * np.random.rand(N), np.random.rand(N),0.4 +0.1 *np.random.rand(N)) g2 = (0.4 +0.3 * np.random.rand(N), 0.5 *np.random.rand(N),0.1 *np.random.rand(N)) g3 = (0.3 *np.random.rand(N),0.3 *np.random.rand(N),0.3 *np.random.rand(N)) data = (g1, g2, g3) colors = ("red" , "green" , "blue" ) groups = ("coffee" , "tea" , "water" ) fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(1 , 1 , 1 , axisbg="1.0" ) ax = fig.gca(projection='3d' ) for data, color, group in zip (data, colors, groups): x, y, z = data ax.scatter(x, y, z, alpha=0.8 , c=color, edgecolors='none' , s=30 , label=group) plt.title('Matplot 3d scatter plot' ) plt.legend(loc=2 ) plt.show()
The plot is created using several steps:
vector creation (g1,g2,g3) list creation (groups) plotting The final plot is shown with plt.show()

Leave a Reply: