Category: pro
Python hosting: Host, run, and code Python in the cloud!
QT GUI
PyQt4 textbox
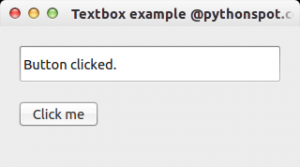
In this article you will learn how to interact with a textbox using PyQt4.
If you want to display text in a textbox (QLineEdit) you could use the setText() method.
Related course:
PyQt4 QLineEdit
The textbox example below changes the text if the button is pressed.
import sys from PyQt4.QtCore import pyqtSlot from PyQt4.QtGui import * # create our window app = QApplication(sys.argv) w = QWidget() w.setWindowTitle('Textbox example @pythonspot.com') # Create textbox textbox = QLineEdit(w) textbox.move(20, 20) textbox.resize(280,40) # Set window size. w.resize(320, 150) # Create a button in the window button = QPushButton('Click me', w) button.move(20,80) # Create the actions @pyqtSlot() def on_click(): textbox.setText("Button clicked.") # connect the signals to the slots button.clicked.connect(on_click) # Show the window and run the app w.show() app.exec_() |
The text field is created with the lines:
textbox = QLineEdit(w) textbox.move(20, 20) textbox.resize(280,40) |
The button (from screenshot) is made with:
button = QPushButton('Click me', w) |
We connect the button to the on_click function by:
# connect the signals to the slots button.clicked.connect(on_click) |
This function sets the textbox using setText().
Qt4 buttons
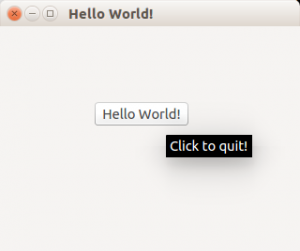
PyQt4 (Qt4) supports buttons through the QPushButton widget.
We extend the code to display a button in the center of the window.
The button will show a tooltip if hovered and when pressed will close the program.
Related course:
PyQt4 button example
The example below adds a button to a PyQt4 window.
#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import sys from PyQt4.QtGui import * # Create an PyQT4 application object. a = QApplication(sys.argv) # The QWidget widget is the base class of all user interface objects in PyQt4. w = QWidget() # Set window size. w.resize(320, 240) # Set window title w.setWindowTitle("Hello World!") # Add a button btn = QPushButton('Hello World!', w) btn.setToolTip('Click to quit!') btn.clicked.connect(exit) btn.resize(btn.sizeHint()) btn.move(100, 80) # Show window w.show() sys.exit(a.exec_()) |
PyQt4 signals and slots
A button click should do something. To do so, you must use signals and slots.
If a user does an action such as clicking on a button, typing text in a box – the widget sends out a signal. Signals can be connected with a slot, that acts as a receiver and acts on it.
import sys from PyQt4.QtCore import pyqtSlot from PyQt4.QtGui import * # create our window app = QApplication(sys.argv) w = QWidget() w.setWindowTitle('Button click example @pythonspot.com') # Create a button in the window btn = QPushButton('Click me', w) # Create the actions @pyqtSlot() def on_click(): print('clicked') @pyqtSlot() def on_press(): print('pressed') @pyqtSlot() def on_release(): print('released') # connect the signals to the slots btn.clicked.connect(on_click) btn.pressed.connect(on_press) btn.released.connect(on_release) # Show the window and run the app w.show() app.exec_() |
Qt4 window
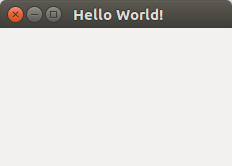
In this tutorial you will learn how to create a graphical hello world application with PyQT4.
PyQT4, it is one of Pythons options for graphical user interface (GUI) programming.
Related course:
PyQt4 window example:
This application will create a graphical window that can be minimized, maximimzed and resized it.
#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import sys from PyQt4.QtGui import * # Create an PyQT4 application object. a = QApplication(sys.argv) # The QWidget widget is the base class of all user interface objects in PyQt4. w = QWidget() # Set window size. w.resize(320, 240) # Set window title w.setWindowTitle("Hello World!") # Show window w.show() sys.exit(a.exec_()) |
The PyQT4 module must be immported, we do that with this line:
from PyQt4.QtGui import * |
We create the PyQT4 application object using QApplication():
a = QApplication(sys.argv) |
We create the window (QWidget), resize, set the tittle and show it with this code:
w = QWidget() w.resize(320, 240) w.setWindowTitle("Hello World!") |
Don’t forget to show the window:
# Show window w.show() |
You can download a collection of PyQt4 examples:
Download PyQT Code (Bulk Collection)
QT4 Messagebox
PyQT4 offers message box functionality using several functions.
Messageboxes included in PyQT4 are: question, warning, error, information, criticial and about box.
Related course:
PyQt4 mesagebox
The code below will display a message box with two buttons:
#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import sys from PyQt4.QtGui import * # Create an PyQT4 application object. a = QApplication(sys.argv) # The QWidget widget is the base class of all user interface objects in PyQt4. w = QWidget() # Show a message box result = QMessageBox.question(w, 'Message', "Do you like Python?", QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No, QMessageBox.No) if result == QMessageBox.Yes: print 'Yes.' else: print 'No.' # Show window w.show() sys.exit(a.exec_()) |
Result:
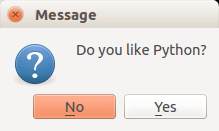
There are different types of messageboxes that PyQT4 provides.
PyQT4 Warning Box
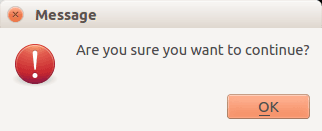
You can display a warning box using this line of code:
QMessageBox.warning(w, "Message", "Are you sure you want to continue?") |
PyQT4 Information box
We can display an information box using QMessageBox.information()
QMessageBox.information(w, "Message", "An information messagebox @ pythonspot.com ") |
Result:
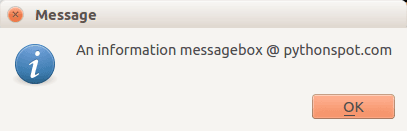
PyQT4 Critical Box
If something goes wrong in your application you may want to display an error message.
QMessageBox.critical(w, "Message", "No disk space left on device.") |
Result:
PyQT4 About box
We have shown the question box above.
QMessageBox.about(w, "About", "An example messagebox @ pythonspot.com ") |
Result:
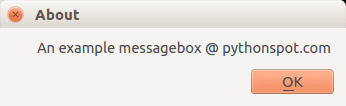
Menu with PyQt4
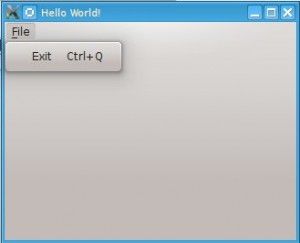
PyQt4 menus appear in the top of the window bar. A menu gives the user control over the application and is often location in the top of the window.
The QMainWindow class creates the main application window. This class has a method named menuBar() which adds the title bar.
Menus can be added to the title bar using addMenu(). Inside each menu you can add a command using the addAction method.
Related course:
PyQt4 menubar
This code will add a menu to your qt4 app:
#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import sys from PyQt4.QtGui import * # Create an PyQT4 application object. a = QApplication(sys.argv) # The QWidget widget is the base class of all user interface objects in PyQt4. w = QMainWindow() # Set window size. w.resize(320, 240) # Set window title w.setWindowTitle("Hello World!") # Create main menu mainMenu = w.menuBar() mainMenu.setNativeMenuBar(False) fileMenu = mainMenu.addMenu('&File') # Add exit button exitButton = QAction(QIcon('exit24.png'), 'Exit', w) exitButton.setShortcut('Ctrl+Q') exitButton.setStatusTip('Exit application') exitButton.triggered.connect(w.close) fileMenu.addAction(exitButton) # Show window w.show() sys.exit(a.exec_()) |
QT4 Widgets
We have various widgets that we can access with PyQT. Including:
- Textbox
- Combobox
- Calendar
For more widgets we suggest using the GUI creation tool covered in the next tutorial.
Related course:
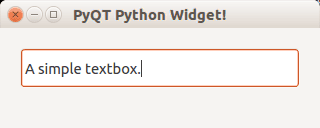
Textbox widget
Input fields are present in nearly every application. In PyQT4 an input field can be created using the QLineEdit() function.
#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import sys from PyQt4.QtGui import * # Create an PyQT4 application object. a = QApplication(sys.argv) # The QWidget widget is the base class of all user interface objects in PyQt4. w = QMainWindow() # Set window size. w.resize(320, 100) # Set window title w.setWindowTitle("PyQT Python Widget!") # Create textbox textbox = QLineEdit(w) textbox.move(20, 20) textbox.resize(280,40) # Show window w.show() sys.exit(a.exec_()) |
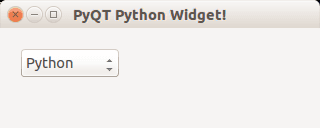
Combobox
A combobox can be used to select an item from a list.
#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import sys from PyQt4.QtGui import * # Create an PyQT4 application object. a = QApplication(sys.argv) # The QWidget widget is the base class of all user interface objects in PyQt4. w = QMainWindow() # Set window size. w.resize(320, 100) # Set window title w.setWindowTitle("PyQT Python Widget!") # Create combobox combo = QComboBox(w) combo.addItem("Python") combo.addItem("Perl") combo.addItem("Java") combo.addItem("C++") combo.move(20,20) # Show window w.show() sys.exit(a.exec_()) |
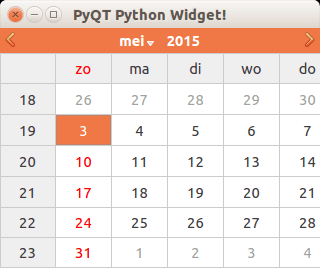
Calendar widget
The PyQT4 library has a calendar widget, you can create it using the QCalendarWidget() call.
#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import sys from PyQt4.QtGui import * # Create an PyQT4 application object. a = QApplication(sys.argv) # The QWidget widget is the base class of all user interface objects in PyQt4. w = QMainWindow() # Set window size. w.resize(320, 240) # Set window title w.setWindowTitle("PyQT Python Widget!") # Create calendar cal = QCalendarWidget(w) cal.setGridVisible(True) cal.move(0, 0) cal.resize(320,240) # Show window w.show() sys.exit(a.exec_()) |
Result: