Tag: matplotlib
Matplotlib Histogram
Matplotlib can be used to create histograms. A histogram shows the frequency on the vertical axis and the horizontal axis is another dimension. Usually it has bins, where every bin has a minimum and maximum value. Each bin also has a frequency between x and infinite.
Related course
Matplotlib histogram example
Below we show the most minimal Matplotlib histogram:
import numpy as np |
Output:
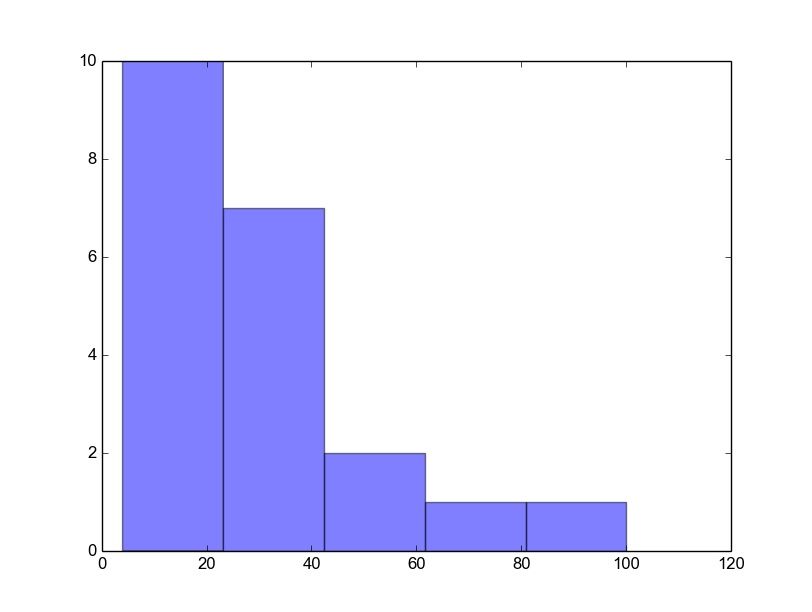
A complete matplotlib python histogram
Many things can be added to a histogram such as a fit line, labels and so on. The code below creates a more advanced histogram.
#!/usr/bin/env python |
Output:
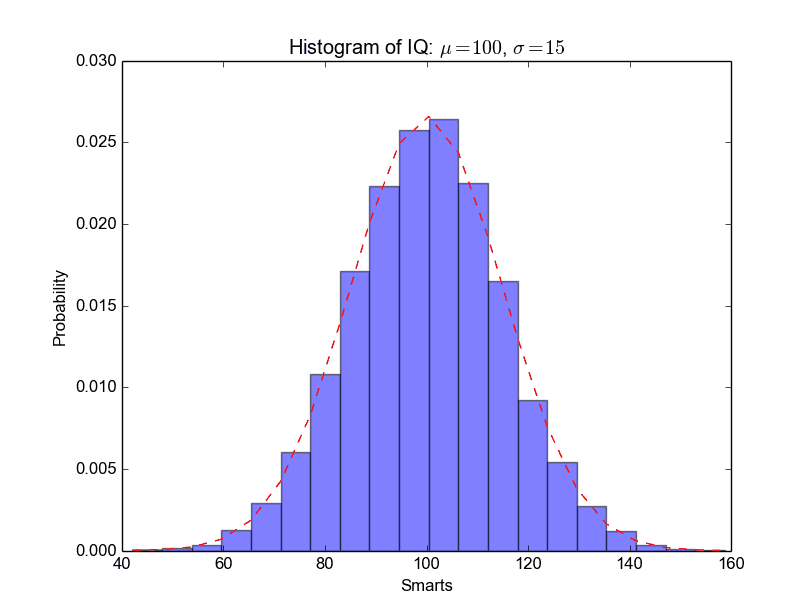
Matplotlib Line chart
Matplotlib Bar chart
Matplotlib may be used to create bar charts. You might like the Matplotlib gallery.
Matplotlib is a python library for visualizing data. You can use it to create bar charts in python. Installation of matplot is on pypi, so just use pip: pip install matplotlib
The course below is all about data visualization:
Related course:
Data Visualization with Matplotlib and Python
Bar chart code
A bar chart shows values as vertical bars, where the position of each bar indicates the value it represents. matplot aims to make it as easy as possible to turn data into Bar Charts.
A bar chart in matplotlib made from python code. The code below creates a bar chart:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt; plt.rcdefaults() |
Output:
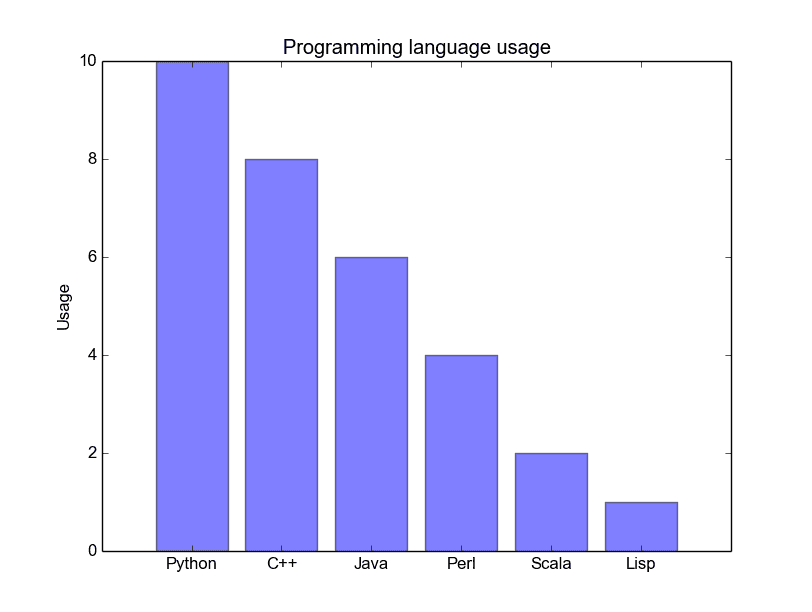
Matplotlib charts can be horizontal, to create a horizontal bar chart:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt; plt.rcdefaults() |
Output:
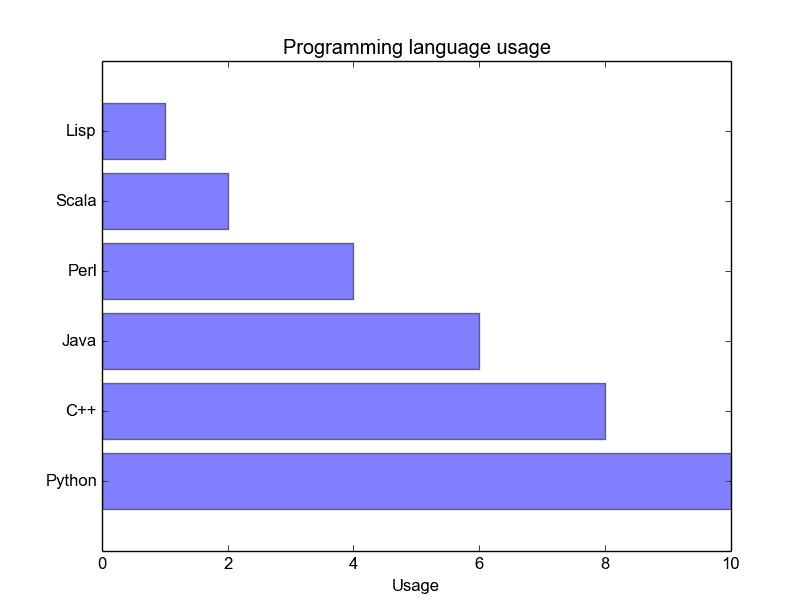
Bar chart comparison
You can compare two data series using this Matplotlib code:
import numpy as np |
Output:
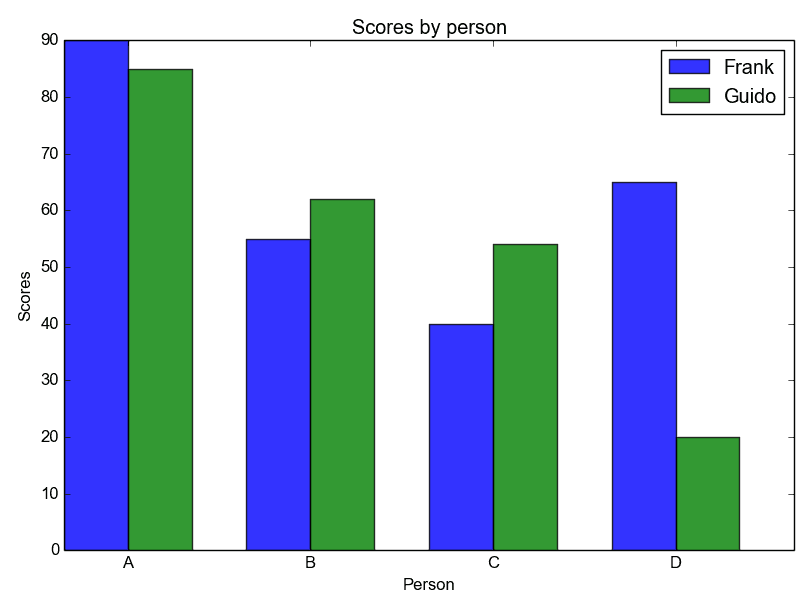
Stacked bar chart
The example below creates a stacked bar chart with Matplotlib. Stacked bar plots show diffrent groups together.
# load matplotlib |
Output:
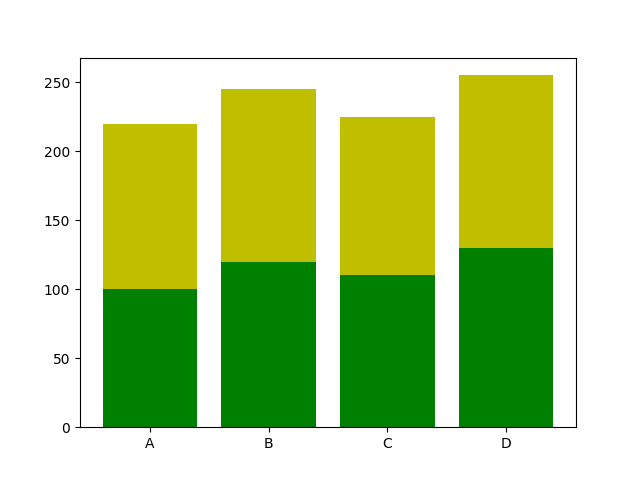
Download All Matplotlib Examples
Matplotlib legend
matplotlib save figure
matplotlib time axis
Matplotlib supports plots with time on the horizontal (x) axis. The data values will be put on the vertical (y) axis. In this article we’ll demonstrate that using a few examples.
It is required to use the Python datetime module, a standard module.
Related course
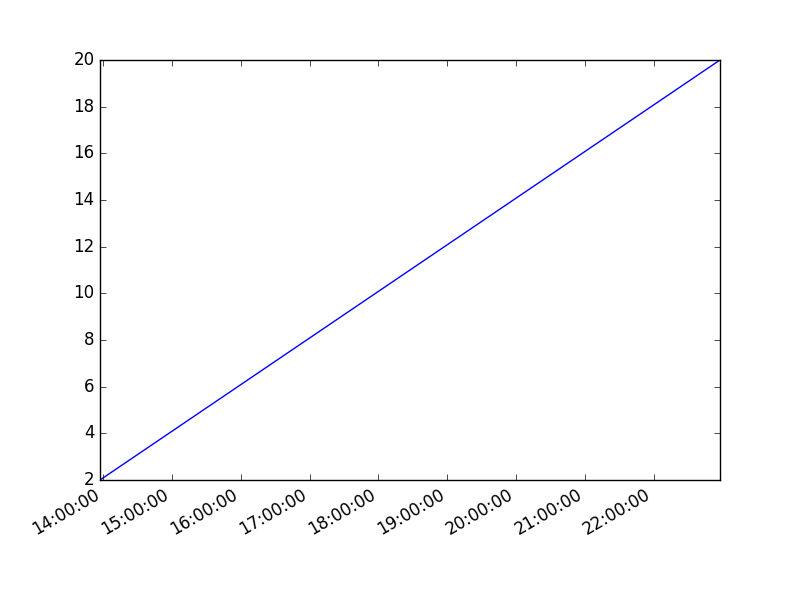
Plot time
You can plot time using a timestamp:
|
If you want to change the interval use one of the lines below:
|
Time plot from specific hour/minute
To start from a specific date, create a new timestamp using datetime.datetime(year, month, day, hour, minute).
Full example:
|
matplotlib heatmap
A heatmap can be created using Matplotlib and numpy.
Related courses
If you want to learn more on data visualization, this course is good:
Heatmap example
The histogram2d function can be used to generate a heatmap.
We create some random data arrays (x,y) to use in the program. We set bins to 64, the resulting heatmap will be 64x64. If you want another size change the number of bins.
|
Result:
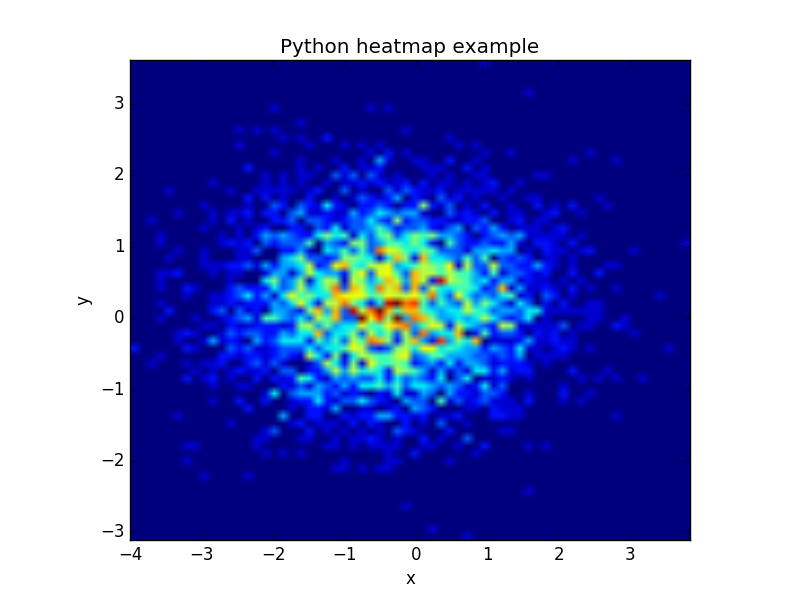
The datapoints in this example are totally random and generated using np.random.randn()
pyqt5 matplotlib
Matplotlib offers powerful visualizations that can be seamlessly integrated into a PyQt5 application. For this, specific libraries and imports are required.
Here’s how you can include Matplotlib plots within a PyQt5 application:
from matplotlib.backends.backend_qt5agg import FigureCanvasQTAgg as FigureCanvas |
The primary component here is a widget named ‘PlotCanvas’ which houses the Matplotlib visualization.
Integration of Matplotlib with PyQt5
The example provided below illustrates the embedding process of a Matplotlib plot within a PyQt5 window. Additionally, we’ll integrate a qpushbutton for demonstration.
import sys |
For those keen on diving deeper into PyQt5’s capabilities, consider downloading these comprehensive PyQT5 Example Codes.
Navigation: