Tag: pyqt5
pyqt statusbar
PyQt5 supports a window status bar. This is a small bar at the bottom of a window that sometimes appears, it can contain text messages. To add a status bar add the line:
|
A statusbar can be added to the main window (QMainWindow). It is one of the methods the class itself contains;
Related course:
Create GUI Apps with PyQt5
PyQt5 statusbar example:
The program below adds a statusbar to a PyQt5 window:
|
The example creates a window (QMainWindow). We set the screen parameters using:
|
Window properties are set in the initUI() method which is called in the constructor. The method:
|
sets the text on the statusbar.
If you are new to programming Python PyQt, I highly recommend this book.
qwidget set position
pyqt tabs
pyqt5 layout
pyqt5 qpainter
pyqt color picker
PyQt5 supports a color picker known as QColorDialog. This dialog is a typical dialog that you would see in a paint or graphics program.
To get a color from PyQt5 dialog simply call:
|
Related course:
PyQt5 color dialog example
The example below opens a QColorDialog after clicking the button (qpushbutton), and returns the selected color.
|
If you are new to programming Python PyQt, I highly recommend this book.
qcolor pyqt5
pyqt drag and drop
Like any modern GUI toolkit, PyQt supports drag and drop. A widget parameter must be set using the setDragEnabled(True) method call. A custom widget should then be set to accept a drop with setAcceptDrops(True).
Related course:
Create GUI Apps with PyQt5
PyQt5 drag and drop example
Drag text from the input field to the label, the label will update its text. Use pyqtslot to connect the action to a function.
|
If you are new to programming Python PyQt, I highly recommend this book.
The textbox is created with the call QLineEdit(). A custom class (CustomLabel) is created that accepts drag and drop. Both events are defined as methods and have their logic executed if the event occurs.
pyqt5 font
PyQt5 comes with a font dialog that you may have seen in a text editor. This is the typical dialog where you can select font, font size, font style and so on. Of course the look and feel depends on the operating system.
To open this dialog import QFontDialog call:
QFontDialog.getFont() |
To use it, import QFontDialog from QtWidgets like this:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QFontDialog |
Related course:
PyQt5 font dialog
The example below opens a font dialog on a button event, the selected font (font family including size) will be returned as a string.
Opening a font dialog is as simple as
def openFontDialog(self): |
Then add a pyqt5 button that opens the dialog. To do that, you need a pyqtslot.
A full code example is shown below
|
If you are new to programming Python PyQt, I highly recommend this book.
pyqt5 matplotlib
Matplotlib offers powerful visualizations that can be seamlessly integrated into a PyQt5 application. For this, specific libraries and imports are required.
Here’s how you can include Matplotlib plots within a PyQt5 application:
from matplotlib.backends.backend_qt5agg import FigureCanvasQTAgg as FigureCanvas |
The primary component here is a widget named ‘PlotCanvas’ which houses the Matplotlib visualization.
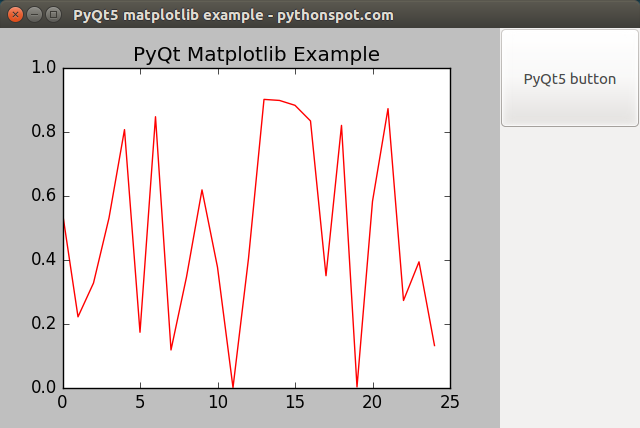
Integration of Matplotlib with PyQt5
The example provided below illustrates the embedding process of a Matplotlib plot within a PyQt5 window. Additionally, we’ll integrate a qpushbutton for demonstration.
import sys |
For those keen on diving deeper into PyQt5’s capabilities, consider downloading these comprehensive PyQT5 Example Codes.
Navigation:
pyqt5 browser
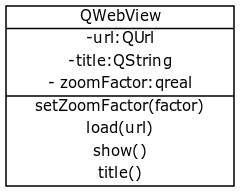
PyQt5 supports a widget that displays websites named QWebView.
QWebView uses the Webkit rendering engine
The web browser engine is used by Safari, App Store and many OS X applications.
The load() method opens the url (QUrl) in the argument. You can create a QUrl using: QUrl(url).
The show() method is required to display the widget.
Related course:
Installation
To use this widget you may need to install an additional package:
|
Read more about PyQt5.
PyQt5 webkit example
The example below loads a webpage in a PyQt5 window.
|
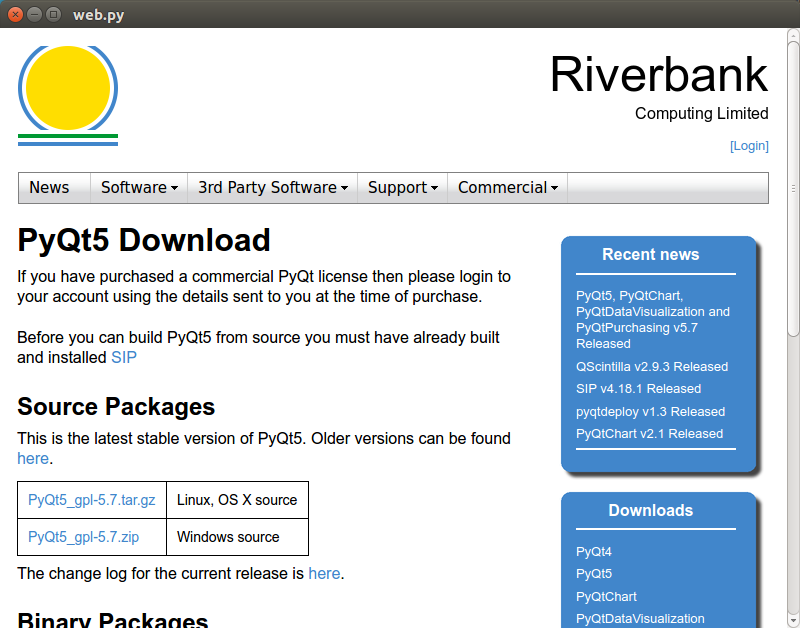
pyqt5 webview
PyQt5 comes with a webkit webbrowser. Webkit is an open source web browser rendering engine that is used by Apple Safari and others. It was used in the older versions of Google Chrome, they have switched to the Blink rendering engine.
Related course:
Create GUI Apps with PyQt5
QWebView
The widget is called QWebView and webpages (HTML content) can be shown through this widget, local or live from the internet.
Methods
The QWebView class comes with a lot of methods including:
- back (self)
- forward (self)
- load (self, QUrl url)
- reload (self)
|
Related course:
Create GUI Apps with PyQt5
